Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
Tags
- solution
- booleanarray
- Java
- 프로그래머스
- 알고리즘
- dp
- Developer
- intarray
- programmers
- hackerrank
- GREEDY
- contentToString
- Poll
- Util
- 2D Array
- lastIndex
- Kotlin
- report
- Recursion
- dynamic programming
- indices
- Queue
- 동적계획법
- heap
- foreach
- 2020
- PriorityQueue
- Main
- sortedBy
- 코틀린
Archives
- Today
- Total
Code in
프로그래머스 동적계획법 N으로 표현 with Kotlin 본문
프로그래머스 동적계획법(Dynamic Programming) N으로 표현 문제입니다.
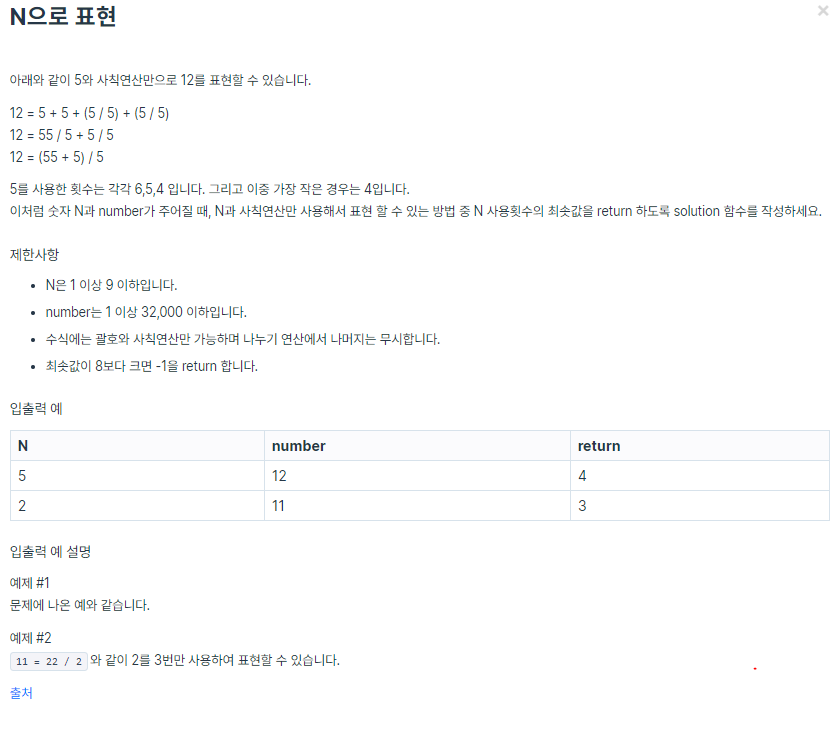
IntelliJ에서의 풀이입니다.
import kotlin.math.pow
val N = 5
val N2 = 2
val N3 = 4
val number = 12
val number2 = 11
val number3 = 17
val N4 = 1
val number4 = 11111
fun solution(N: Int, number: Int): Int {
data class ns(val N: Int, val C: Int)
val candidate: MutableSet<ns> = mutableSetOf<ns>(ns(N, 1))
// N 1번 사용한 상태로 시작
var tmp1: ns
var tmp2: ns
var tmp3: ns
var lastindex1: Int
var lastindex2: Int
var NN: Int
if (N == number) return 1
for (i in 2..8) {
// NN
NN = 0
for (k in 0 until i) NN += N * 10.0.pow(k).toInt()
if (NN == number) return i
candidate.add(ns(NN, i))
// 추가
lastindex1 = candidate.indexOfLast { it.C < i }
for (j in 0 until lastindex1) {
tmp1 = candidate.elementAt(j)
lastindex2 = candidate.indexOfLast { it.C <= i - tmp1.C }
for (k in 0..lastindex2) {
tmp2 = candidate.elementAt(k)
if (tmp1.C + tmp2.C > i) continue
// +
tmp3 = ns(tmp1.N + tmp2.N, tmp1.C + tmp2.C)
if (tmp3.N == number) return tmp3.C
else candidate.add(tmp3)
// -
tmp3 = ns(tmp1.N - tmp2.N, tmp1.C + tmp2.C)
if (0 < tmp3.N)
if (tmp3.N == number) return tmp3.C
else candidate.add(tmp3)
tmp3 = ns(tmp2.N - tmp1.N, tmp1.C + tmp2.C)
if (0 < tmp3.N)
if (tmp3.N == number) return tmp3.C
else candidate.add(tmp3)
// *
tmp3 = ns(tmp1.N * tmp2.N, tmp1.C + tmp2.C)
if (tmp3.N == number) return tmp3.C
else candidate.add(tmp3)
// /
tmp3 = ns(tmp1.N / tmp2.N, tmp1.C + tmp2.C)
if (0 < tmp3.N)
if (tmp3.N == number) return tmp3.C
else candidate.add(tmp3)
tmp3 = ns(tmp2.N / tmp1.N, tmp1.C + tmp2.C)
if (0 < tmp3.N)
if (tmp3.N == number) return tmp3.C
else candidate.add(tmp3)
}
}
candidate.sortedBy { it.C }
}
return -1
}
fun main() {
println(solution(N, number)) //4 // 5, 12 = (55 + 5)/5
println(solution(N2, number2)) //3 // 2, 11 = 22/2
println(solution(N3, number3)) //4 // 4, 17 = 4*4 + 4/4
println(solution(N4, number4)) // 5
}
URL: https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/42895?language=kotlin
코딩테스트 연습 - N으로 표현
programmers.co.kr
candidate라는 Set과 반복문을 사용하여 하나씩 추가하면서 해결했는데,
프로그래머스에서 다른 사람의 풀이들을 보니 재귀 함수로도 풀이할 수 있었습니다.
더보기
재귀 함수를 사용한 다른 사람의 풀이:
class Solution {
var min: Int = -1
fun solution(N: Int, number: Int): Int {
dfs(N, number, 0, 0)
return min
}
fun dfs(N: Int, number: Int, count: Int, prev: Int) {
var tmpN = N
if (count > 8) {
min = -1
return
}
if (number == prev) {
if (min == -1 || min > count) min = count
return
}
for (i in 0..(8-count-1)) {
dfs(N, number, count+i+1, prev-tmpN)
dfs(N, number, count+i+1, prev+tmpN)
dfs(N, number, count+i+1, prev*tmpN)
dfs(N, number, count+i+1, prev/tmpN)
tmpN = tmpN * 10 + N
}
}
}'알고리즘 스터디_문제풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 프로그래머스 깊이/너비 우선 탐색 네트워크 with Kotlin (1) | 2020.08.26 |
|---|---|
| 프로그래머스 깊이/너비 우선 탐색 타겟 넘버 with kotlin (1) | 2020.08.25 |
| 프로그래머스 탐욕법(Greedy) 섬 연결하기 with Kotlin (2) | 2020.08.18 |
| 프로그래머스 탐욕법(Greedy) 조이스틱 with Kotlin (1) | 2020.08.17 |
| 프로그래머스 탐욕법(Greedy) 큰 수 만들기 with Kotlin, 테스트 케이스 추가 (1) | 2020.08.16 |
Comments




